Termite Control Service in
bangalore
Termites also known as white ants live as a social colony consisting of queen, king, solders and
workers. Queen controls
and runs the society as leader for food, security and reproduction. Workers make the tunnel path
to harvest cellulose
food in any kind of materials in any place.
Termites mostly feed on dead plant material and cellulose, generally in the form of wood, leaf
litter, soil, or animal
dung.
Types of Termites:
- Dry wood termites or Wood nesting termites:
- Very rarely found
- Nest in wooden blocks
- Small colony
- Presence is confirmed when poppy seed like droppings are seen in the vicinity of the
affected area.
- Sub-terranean termites or Soil nesting termites
- Always nest in soil
- Construct mud tunnels
- Survive on old debris, stumps, etc.
- Only insect that is capable of digesting cellulose
- Causes enormous damages to property resulting in heavy losses
- It is a worldwide problem
Caste System:
Termites show 4 castes distinctly:
- Queen – Fertile females
Termite queens have the longest lifespan of any insect in the world, with some queens
reportedly living up to 30 to 50
years. The queen of the colony is responsible for egg production for the colony.
- King – Fertile males
The king mates with the queen for life.
- Soldiers – Protect colony
Soldiers have enlarged heads, that are hard and yellow to brown in color, with large
mandibles that are used to puncture
termite enemies, primarily ants. The soldier caste has anatomical and behavioral
specializations, and their sole purpose
is to defend the colony.
- Workers – Damage property (Real Pests)
Are Blind and Sterile, Construct mud tunnel, causes damage to property and are millions
in number. Worker termites
undertake the most work within the colony such as foraging, food storage, and brood and
nest maintenance. Workers are
tasked with the digestion of cellulose in food and are thus the most likely caste to be
found in infested wood.
Most worker and soldier termites are completely blind as they do not have a pair of eyes.
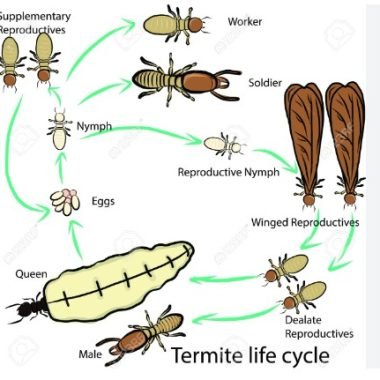
Life Cycle:
The life cycle of a termite begins with an egg, and goes through incomplete metamorphosis.
Egg to nymph and adult stages. Nymphs resemble small adults and go four moulting stages and
nymphs go through three.
Nymphs first moult into workers, and then some workers go through further moulting and become
soldiers or alates.
Termite Communication:
Most termites are blind, so communication primarily occurs through chemical, mechanical and
pheromonal cues. . The most
common way of communicating is through antennation. Termite antennae have a number of functions
such as the sensing of
touch, taste, odours (including pheromones), heat and vibration.
Termite identification and symptoms:
Aim of a termite inspection is to determine:
The location of all areas of termite activity
- The location of all areas of termite activity
- The points of entry into the structure
- Potential areas for re-infestation
- The potential nest sites
- The areas posing difficulties or limitations for treatment
or limitations for treatment
An inspector must have a good knowledge of the following:
- Termite biology and behavior
- Treatment practices
- Building construction
Route of entry:
- Along the drainage pipes
- Through walls
- Electrical cabling
- Conduit pipes
- Lift well
Termite Inspection
Termite management is challenging. Successful termite control begins with thorough termite
inspection. Termites are not
easy to detect
Inspecting the Interior:
Key inspection areas:
- Flooring:
- Gaps or loose tiles
- Carpet – wooden strips
- Wall surfaces:
- Around windows and doorways
- Near plumbing and electrical wiring
- At the ceiling line
- Bookcases,
- Air-conditioning units,
- Plumbing areas and drains
- Power sockets, electrical conduit, telephone and television cables
Inspecting the Ceiling/Roof:
Key Inspection Areas:
- Wooden beams, roof rafters, wooden slats
- Cabling
- Plasterboard
- Cracks in the wall
For ROW houses there can be a common roof void
This provides termites with easy access from one structure to another. Consider informing the
neighbors if an
infestation is found
Inspection of Adjoining Structures:
Termites can also infest adjoining structures such as garages, sheds and carports.
Termites may gain access through the perimeter expansion joint or through ceiling or roof voids.
Inspection of Sub-structures
- The entire perimeter (where accessible), Foundation walls, wooden beams, joists and
sub-flooring timbers
- Plumbing pipes,
- Stairs Areas:
- Patios,
- Earth-filled porches
- Stacked timber, wood debris, foam boards, stumps, stakes, cardboard,
Inspection of Basements:
- Suspended ceiling
- Wood at the base of stairs,
- Support posts,
- Partitions,
- Doors
- Plumbing entries
- Settlement cracks in floor or wall
Termite Inspection Report:
The report should clearly record:
- Evidence of live termites
- Evidence of previous but no longer active termite infestations
- Areas inaccessible to inspection
- Damage found
- Suspected areas of termite activity and damage
- Areas where termite treatment may be difficult
- Areas prone to termite attack (i.e. humid areas., etc.)
Successful termite control process include:
- Thorough termite inspection.
- Use of precise diagnostic techniques and identification tools like Moisture meter, Acoustic
Devices, Movement Detection Devices (TERMITRAC) etc.
- Marking the root cause.
- Deciding the treatment with base plan of building is most essential as termites may re-enter
along the drainage pipes, electrical cabling, and conduit pipes and lift well.
- Apart from building area the perimeter ground will also be treated for 100% success.
Post Anti-termite treatment:
- It is a post construction termite control service for existing buildings /structures
- DRILL-FILL-SEAL technique is adopted with new generation systemic termiticides used as
filling components.
- No damages to other structures.
- Can be applied to any kind of flooring materials without much damage.
- Perimeter areas may also be treated if required.
Pre-Anti-termite treatment:
- It is a pre-construction termite control service for buildings /structures under
construction with 10- 15 years protection against termites.
- Very effective as it creates a uniform chemical barrier around the building..
- Applied in three stages as: – Stage1-Foundation, Stage2- Flooring and Stage3- Perimeter
surrounding the building.
